单一指数模型
Single-index model
单一指数模型(single-index model (SIM))是简单资产定价模型,它通常用于金融行业对于一个股票的风险和回报的评估。
These equations show that the stock return is influenced by the market (beta), has a firm specific expected value (alpha) and firm-specific unexpected component (residual). Each stock's performance is in relation to the performance of a market index (such as the All Ordinaries). Security analysts often use the SIM for such functions as computing stock betas, evaluating stock selection skills, and conducting event studies.
单一指数模型假设
为了便于分析,单一指数模型假设只有一种宏观因素会引起股票收益风险,可以用一个市场指数的收益率来表示,例如标普指数500(S&P 500)。根据这个模型的假设,任何股票的收益都可以分解为个别股份剩余收益的期望(这里用一个公司特指的因子α表示)、影响市场的宏观事件的收益和不可预测的只影响公司的微观事件组成。
βi(rm − rf) 表示股票影响下的市场运动,ei表示公司因素影响下的债券风险。
宏观事件,例如利率的变化、劳动力成本的变化,会引起影响整个股票市场的收益的系统风险。公司特指事件是会引起特定公司收益变化的微观事件,例如重要人物的去世或者降低公司的信用等级都会影响公司的收益,但是对整个经济的影响是微不足道的。在一个投资组合里,由公司特指因素引起的非系统风险可以通过离散化降低为0。
这个指数模型基于下列假设:
大部分的股票有正的协方差因为他们对于宏观事件反应相似。然而,一些公司对于这些因素的敏感程度大于别的公司,由系数β来控制这个敏感程度。债券之间的协方差是由于对宏观事件的不同造成的。所以,每只股票的协方差等于他们的β相乘。 Cov(Ri, Rk) = βiβkσ2.
最后一个方程大大降低了协方差的计算量,否则,投资组合里债券的协方差必须用历史收益计算,每一债券的必须单独计算。有了这个方程,只需要β和市场的方差就可以。于是单一指数模型大大的降低了计算量。
单一指数模型(single-index model (SIM))是简单资产定价模型,它通常用于金融行业对于一个股票的风险和回报的评估。

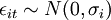
These equations show that the stock return is influenced by the market (beta), has a firm specific expected value (alpha) and firm-specific unexpected component (residual). Each stock's performance is in relation to the performance of a market index (such as the All Ordinaries). Security analysts often use the SIM for such functions as computing stock betas, evaluating stock selection skills, and conducting event studies.
单一指数模型假设
为了便于分析,单一指数模型假设只有一种宏观因素会引起股票收益风险,可以用一个市场指数的收益率来表示,例如标普指数500(S&P 500)。根据这个模型的假设,任何股票的收益都可以分解为个别股份剩余收益的期望(这里用一个公司特指的因子α表示)、影响市场的宏观事件的收益和不可预测的只影响公司的微观事件组成。
βi(rm − rf) 表示股票影响下的市场运动,ei表示公司因素影响下的债券风险。
宏观事件,例如利率的变化、劳动力成本的变化,会引起影响整个股票市场的收益的系统风险。公司特指事件是会引起特定公司收益变化的微观事件,例如重要人物的去世或者降低公司的信用等级都会影响公司的收益,但是对整个经济的影响是微不足道的。在一个投资组合里,由公司特指因素引起的非系统风险可以通过离散化降低为0。
这个指数模型基于下列假设:
大部分的股票有正的协方差因为他们对于宏观事件反应相似。然而,一些公司对于这些因素的敏感程度大于别的公司,由系数β来控制这个敏感程度。债券之间的协方差是由于对宏观事件的不同造成的。所以,每只股票的协方差等于他们的β相乘。 Cov(Ri, Rk) = βiβkσ2.
最后一个方程大大降低了协方差的计算量,否则,投资组合里债券的协方差必须用历史收益计算,每一债券的必须单独计算。有了这个方程,只需要β和市场的方差就可以。于是单一指数模型大大的降低了计算量。
附件列表
词条内容仅供参考,如果您需要解决具体问题
(尤其在法律、医学等领域),建议您咨询相关领域专业人士。
