Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization - EBITDA
An indicator of a company's financial performance which is calculated in the following EBITDA calculation:
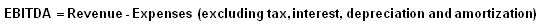
EBITDA is essentially net income with interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization added back to it, and can be used to analyze and compare profitability between companies and industries because it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
|||This is a non-GAAP measure that allows a greater amount of discretion as to what is (and is not) included in the calculation. This also means that companies often change the items included in their EBITDA calculation from one reporting period to the next.
EBITDA first came into common use with leveraged buyouts in the 1980s, when it was used to indicate the ability of a company to service debt. As time passed, it became popular in industries with expensive assets that had to be written down over long periods of time. EBITDA is now commonly quoted by many companies, especially in the tech sector - even when it isn't warranted.
A common misconception is that EBITDA represents cash earnings. EBITDA is a good metric to evaluate profitability, but not cash flow. EBITDA also leaves out the cash required to fund working capital and the replacement of old equipment, which can be significant. Consequently, EBITDA is often used as an accounting gimmick to dress up a company's earnings. When using this metric, it's key that investors also focus on other performance measures to make sure the company is not trying to hide something with EBITDA.
EBITDA is essentially net income with interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization added back to it, and can be used to analyze and compare profitability between companies and industries because it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
|||This is a non-GAAP measure that allows a greater amount of discretion as to what is (and is not) included in the calculation. This also means that companies often change the items included in their EBITDA calculation from one reporting period to the next.
EBITDA first came into common use with leveraged buyouts in the 1980s, when it was used to indicate the ability of a company to service debt. As time passed, it became popular in industries with expensive assets that had to be written down over long periods of time. EBITDA is now commonly quoted by many companies, especially in the tech sector - even when it isn't warranted.
A common misconception is that EBITDA represents cash earnings. EBITDA is a good metric to evaluate profitability, but not cash flow. EBITDA also leaves out the cash required to fund working capital and the replacement of old equipment, which can be significant. Consequently, EBITDA is often used as an accounting gimmick to dress up a company's earnings. When using this metric, it's key that investors also focus on other performance measures to make sure the company is not trying to hide something with EBITDA.
附件列表
词条内容仅供参考,如果您需要解决具体问题
(尤其在法律、医学等领域),建议您咨询相关领域专业人士。
